Log Winder, Small Roll Center Winder,
and Small Roll Surface Winder
Log Winders, Small Roll Center Winder, and Small Roll Surface Winder
Textile Surface Winders and More
We offer shaftless surface winders designed for winding textiles, coated fabrics, carpets, and nonwoven products with unmatched precision. Our equipment has various features and customizable options to meet your requirements and elevate your production process.
Surface Textile Winders and More
We offer shaftless surface log winders designed for winding textiles, coated fabrics, carpets, and nonwoven products with unmatched precision. Our equipment has various features and customizable options to meet your requirements and elevate your production process.
- Product roll location controlled by side panels or shafting mounted in shaft guides.
- Either pivot mount or counter balanced rider roll mounted in linear slides.
- Pneumatically actuated tilt and roll dump off.
- An optional dual motor arrangement is offered to control roll packing.
- Closed loop load cell and edge guiding are offered.

Shaftless Log Winders
Our shaftless log winders are specifically designed to wind up many custom web products with automatic cut-to-length functionality and automated finished product roll removal.
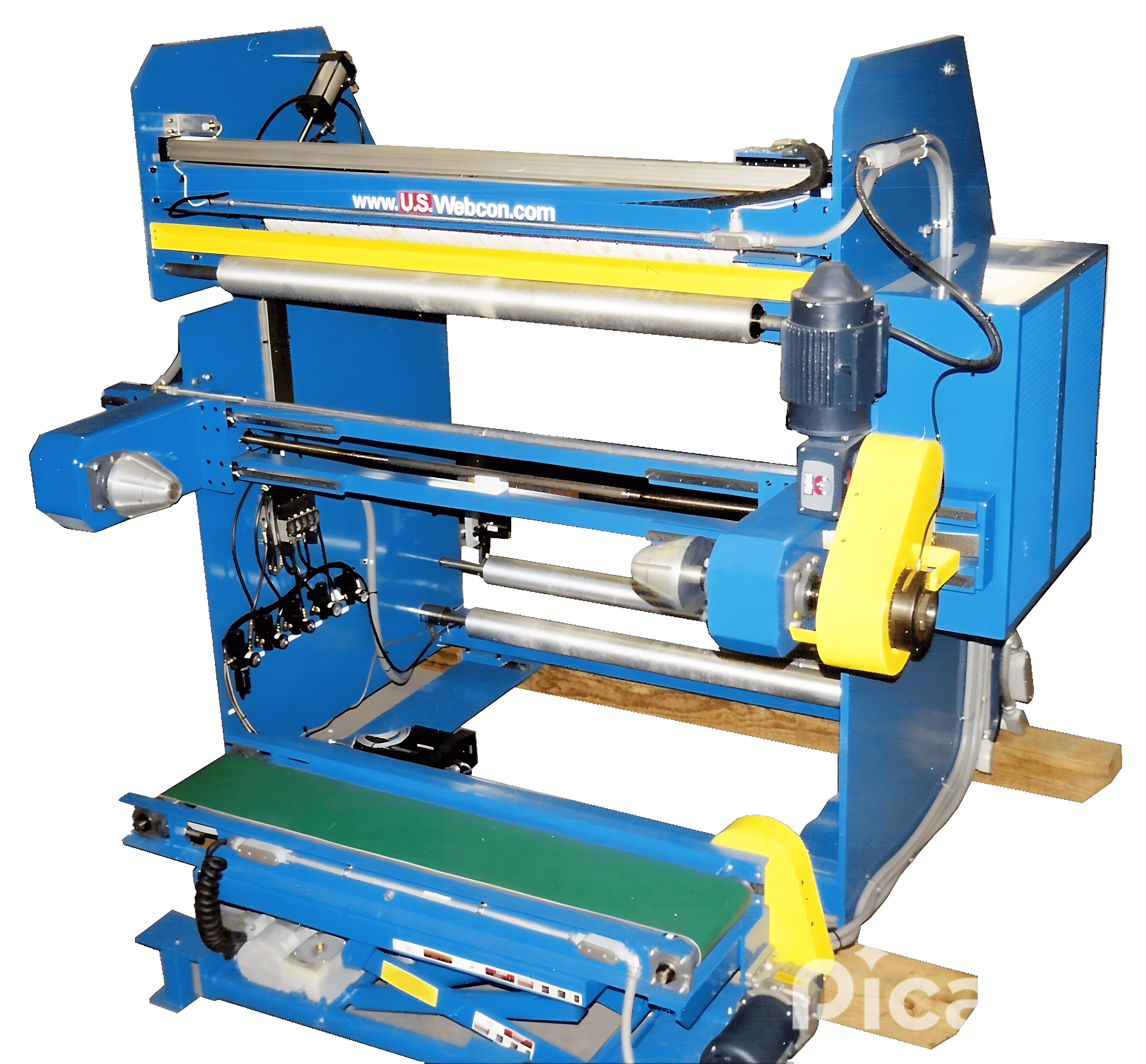
Shaftless Log Winders
Our shaftless log winders are designed to efficienctly wind small log rolls with many features and options to fit your specific appications:
- Traveling knife cut off the web off with a square edge.
- Counters to wind the roll length to the right length.
- Hydraulic lift tables to hold the roll while unloading.
- Conveyors to bring the roll to an offline position for packaging.
- Closed loop load cells for tension control and edge guiding.
Small Roll Surface Log Winders
Our small roll surface log winders are designed to break down large master rolls of paper, film and nonwoven material into small consumer rolls or rolls that can be handled easily by installers. They feature an integral unwind with closed loop load cell tension control and edge guiding.
Surface Log Winders
Our shaftless surface log winders are designed to efficienctly wind small log rolls with many features and options to fit your specific appications:
- Manually operated razor knife or a pneumatically operated traveling cut off knife.
- Counters to wind the roll length to the right length.
- V-tray in the front to catch the roll while cutting the web and placing a core.
- Pneumatically offloaded top rider roll creates a firm roll.
- Closed loop load cells for tension control and edge guiding.
- If you would like to see one of our specialty web center folders?
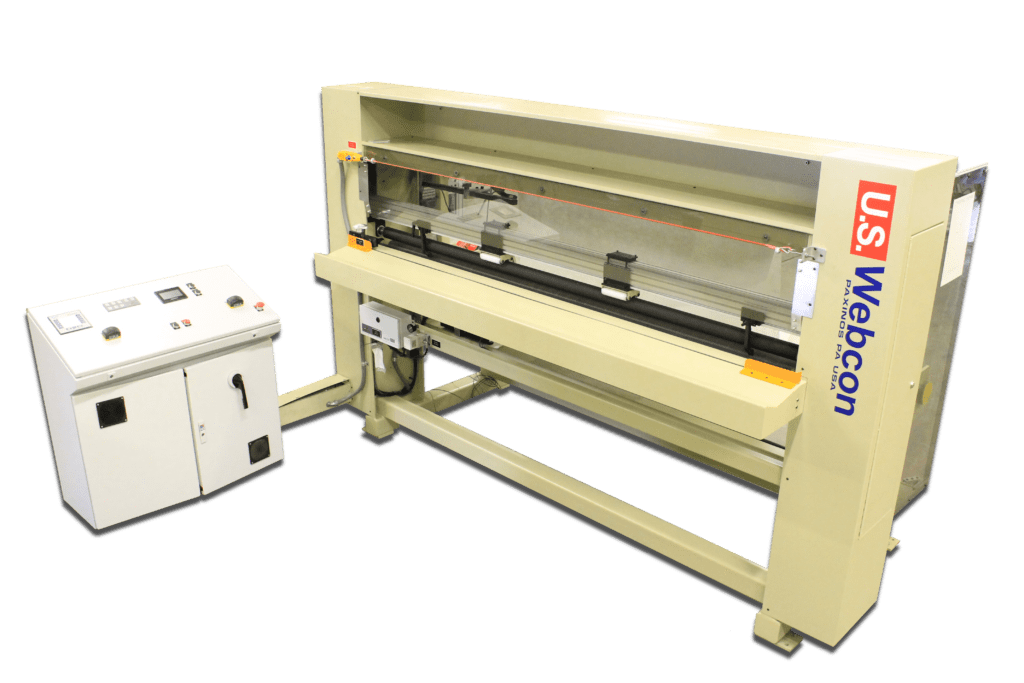
Cantilevered Center Log Winder
Our small roll cantilevered center log winders are designed to break down large master rolls of paper, film and nonwoven material into small consumer rolls or rolls that can be handled easily by the users.
Cantilevered Log Center Winders
Our cantilevered log winders are designed to efficienctly wind small log rolls with many features and options to fit your specific appications:
- Traveling knife to cut off the web off with a square edge.
- Counters to wind the roll length to the right length
- Two button hand switch for operator safety.
- Closed loop load cells for tension control and edge guiding.
- To see some more cantilevered and narrow web winders go to our narrow web handling page.

Complete Line of Small Roll Log Winders for Diverse Production Needs
Our company prides itself on its comprehensive line of standalone small roll winders, log winders, and breakdown winders to meet your unique production.
Contact U.S. Webcon
Discover the unmatched precision and customizable options of our wide range of winders. Get in touch with our team to discuss your specific requirements.
What is a log winder?
A log winder is a machine used to wind large rolls of material, often called “logs,” in the converting industry. It is designed to wind rolls of paper, film, or nonwoven materials into larger rolls before they are cut or processed further.
How do log winders work?
- Log winders typically feature a core and a spindle around which the material is wound. The material is pulled through rollers, and as the log winder rotates, the material is wound onto the core to form a large roll. The machine applies controlled tension to ensure the roll is even and stable.
How is a log winder different from a surface winder?
-
-
The primary difference is that log winders are designed to handle large logs or rolls, typically used for heavy-duty applications. In contrast, surface winders are more focused on winding smaller rolls with high precision and are better suited for delicate materials.
-
-
-
What are the different types of log winders?
. Shafted Log Winders
-
Description: These are the traditional type of log winders that utilize a central shaft to support and drive the core around which the material is wound. The shaft holds the core, and the material is wound onto it as the shaft rotates.
-
How It Works:
-
A shaft is inserted into the core of the roll, and the material is wound around it.
-
The core and material are then rotated by the winder’s drive mechanism, and tension is controlled through the nip rollers and the shaft.
-
-
Advantages:
-
Relatively simple design and widely used in the industry.
-
Suitable for a range of materials, including thicker paper and film.
-
Common in applications where the rolls are expected to have a uniform density and smooth surface.
-
-
Limitations:
-
Requires precise alignment to prevent material from slipping on the shaft.
-
Higher maintenance due to the use of shafts, which can wear over time.
-
Slower loading and unloading of rolls since the shaft must be removed and replaced for each new roll.
-
-
Applications:
-
Paper mills, packaging, film, and foil production.
-
2. Shaftless Log Winders
-
Description: Shaftless log winders do not require a central shaft for supporting the core. Instead, they use air shafts or other mechanical systems to hold the material and core in place while winding.
-
How It Works:
-
Air shafts (or other forms of core support) are used to expand and grip the inside of the core, allowing the material to be wound onto the roll without a central shaft.
-
The core is placed on the winding machine, and air pressure or mechanical means expands the core to hold it in position. The material is then wound around the core as the winder operates.
-
-
Advantages:
-
Faster roll changes since there’s no need to insert or remove a central shaft.
-
Easier handling of larger or heavier rolls.
-
Less wear and tear on the equipment since there’s no shaft to damage the core.
-
Reduced downtime and improved efficiency, especially in high-volume production environments.
-
-
Limitations:
-
Potentially higher initial cost compared to shafted winders.
-
Requires more precise control over tension to ensure uniformity during winding.
-
-
Applications:
-
Used in high-speed, high-volume operations where quick roll changes and reduced downtime are critical, such as in paper, textiles, and nonwoven fabric industries.
-
3. Center Winder (Core Winder)
-
Description: A center winder uses a rotating core at the center of the log around which material is wound. This type of winder is typically used in processes where the core is a key part of the winding operation, such as in tissue or paper manufacturing.
-
How It Works:
-
The core is placed at the center of the winding machine, and material is wound directly onto it. The core remains stationary while the material winds around it.
-
Tension is controlled during the winding process using rollers and the drive system.
-
-
Advantages:
-
Ideal for materials that require a solid core, such as tissue paper or other packaging materials.
-
Suitable for slower-speed processes where the focus is on high-quality, consistent rolls.
-
-
Limitations:
-
Less efficient in high-speed applications compared to shaftless or surface winders.
-
-
Applications:
-
Used in specialized paper and tissue roll production.
-
-
How do log winders affect the quality of the final product?
I am a so called subtitle.Log winders help ensure consistent roll quality by controlling tension during the winding process. This leads to uniform roll density, reducing defects in the final product and increasing efficiency in downstream processing.





